In Human Resources
Is capital goods a good career? Yes, it is. Working in the capital goods industry can be a great career choice.

Management

Jobs in capital goods are highly specialized and offer a wide range of job options. In addition to a high salary, capital goods positions also offer a wide range of abilities that can be used in different technological areas.
For those with a passion for computers and science, the capital goods business is an ideal place to pursue a career. Thus, we will talk about the capital goods industry, which has many job opportunities and is always in high demand.

What are Capital Goods?
Capital goods are physical assets that a company uses in the production process to produce products and services that will later be used by consumers. Capital goods include buildings, machinery, equipment, vehicles and tools. Capital goods are not finished goods; they are used to manufacture finished goods.
Capital Goods examples
- Capital goods are physical assets that a company uses in the production of products and services that will later be used by consumers.
- Capital goods include fixed assets such as buildings, machinery, equipment, vehicles and tools.
- Capital goods are also produced for the service sector, including hair clippers used by hairdressers and coffee machines for coffee shops.
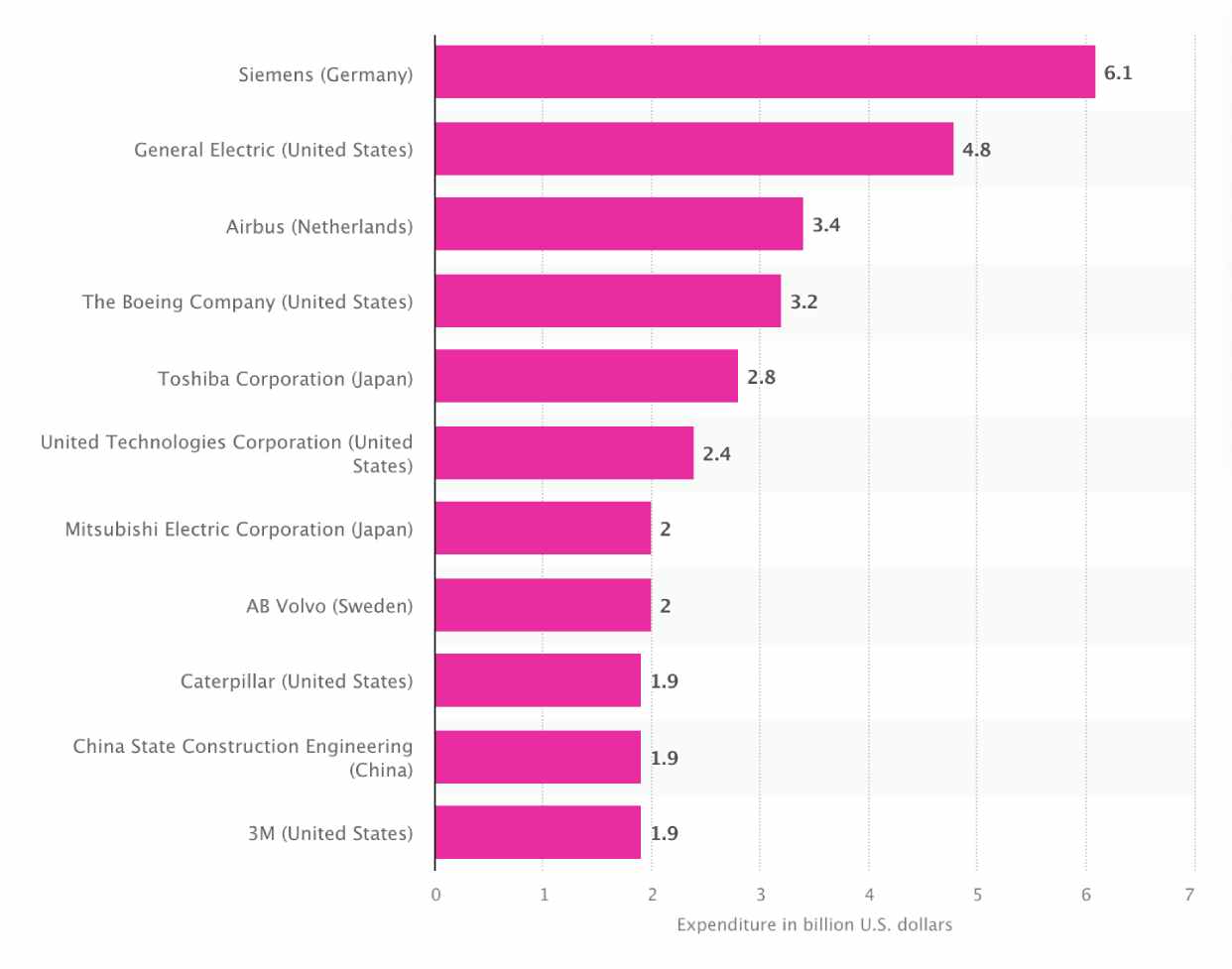
Leading capital goods companies with the highest spending on R&D (2018). Sourcse: Bloomberg; Thomson Reuters; Capital IQ; PwC; Statista.
What types of jobs exist in the capital goods industry?
Some of the most common questions people ask before starting a career in the capital goods industry are the number of jobs available in this field, the nature of the opportunities and their respective salaries.
At this point, we will look at the most in-demand roles in the capital goods sector.
1. Process Engineer
They are experts in maintaining machines and detecting any faults and deficiencies in the operation. Other work they do includes checking that the production process is working well and fixing any problems that may arise.
2. Marketing manager
The job of marketing managers in manufacturing companies is to create and implement marketing strategies that will attract potential customers and retain those they already have.
For the most part, these are marketing or business graduates with at least a few years of experience.
3. Warehouse worker
Warehousing goods, packing, ordering goods and preparing orders for delivery are just some of the duties of the person in this position.
Working in a warehouse can be tiring, but the work itself is fascinating.
4. Managerial engineer

What do capital goods jobs pay? Managerial engineer
Among the highest paid professionals in the capital goods sector are management engineers.
As the name implies, the main responsibility of the engineer-manager is to oversee and coordinate the engineering efforts of the firm.
The product developer, tester and manufacturer are all examples of what they also do.
5. Technician-technologist
Their responsibilities include checking and certifying products and checking the performance of machines. The main responsibility of this position is the maintenance of production equipment.
6. Senior Mechanical Engineer
This is one of the most lucrative positions in the facilities business. Candidates for this position should have at least ten years of relevant work experience.
Senior mechanical engineers are involved in hydraulic design and construction. They are also responsible for creating and evaluating mechanical gadgets.
7. Assembler
These are very skilled people who have to oversee the flow of materials, from raw materials to the finished product.
8. Electrical engineer
The job of an electrical engineer is to plan, build, evaluate and oversee the construction of electronic systems such as engine drives, detection technology and GPS, satellite communications and power generators. Electrical systems for vehicles and aircraft are also at the heart of their work.
9. Computer-aided design specialist
What do capital goods jobs pay: CAD specialist
They use CAD applications to create goods and manufacture them.
10. Research and development manager
Another highly paid and coveted profession is that of research and development manager for capital goods. Research and development (RD) initiatives are their main focus.
They are responsible for overseeing and coordinating their activities to ensure that the needs of the group are met and that promising new products are profitable.
They are also involved in developing and implementing RD strategies and processes.
11. Robotics engineer

What do capital goods jobs pay: Robotics engineer
Designing mechanics and electrical devices is his or her job.
Those who work in robotics don't just make good money. They are some of the happiest technical workers in the world because of their working conditions and the use of their talents.
They received an average score of 4.2 out of 5, which placed them in the top 4% of all jobs surveyed.
12. Quality control manager
The job of a quality control manager is to supervise employees and evaluate business development operations to ensure that products meet performance and productivity criteria.
In addition, the quality control manager works closely with customers to ensure that finished products meet their expectations.
13. Production manager
He or she is responsible for the arrangement of machines and the flow of the production process. The day-to-day operations of the production plant are under the control of the production managers of the company.
They are responsible for all aspects of the production process, including coordination, planning and execution. The production manager may be responsible for the whole facility or just part of it.
14. Industrial designer
Automobiles, appliances, toys and other industrial products are the work of industrial designers. These people mix art, commerce and technology to create goods that appeal to people.
As far as the means of production are concerned, a university degree in industrial design and several years' experience are necessary.
15. Sales engineer
Capital goods companies hire sales engineers who are experts in selling cutting-edge technology and scientific goods.
As a result, sales engineers use their knowledge of technology to show the benefits of the company's products and services to people who can buy them.
16. Business development manager
In a typical capital goods company, business development managers are responsible for organising, managing and overseeing the company's business development activities.
Do Capital Goods Jobs Pay well?
It depends on your educatiion, skills, experience and qualification. In general, one can expect an average salary of $50,000 – $90,000 per year. For instance, some stats shows an Engineering Manager in the United States earns between $120,000 and $160,000 per year in 2022. Electrical engineers are typically very well paid: their earnings in the U.S. are from $63k to $80k per year.
Another example is civil engineer job, which normally lets to earn about $67,000 per year in a manufacturing company.
Some other stats:
- The average salary of a Manufacturing Engineer is $93,000 a year
- Maintenance Engineer earns about $60,000 – $70,000 per year
- Sales Engineer can expect more than $120,000 yearly income
- Marketing Manager yearly wage can be around $150,000
What are the capital goods industries?
Many industries and sectors make up the capital goods market. Some of the most prominent include the following.
1. Chemical industry

What do capital goods jobs pay in Chemical industry
Consumer goods such as paints, cleaning products, surfactants and some natural resources such as mineral deposits, oils and natural gas are produced using chemicals in the chemical industry.
2. Electronics industry
This capital goods industry sector includes a wide range of sub-sectors such as processors, telecommunications, electronics for personal and household use, and industrial electrical products.
Many capital goods from the electronics industry are exported to other industries for use in the production of electronic goods.
3. Textile industry
Flax, silk and nylon are some of the products produced in the textile industry. Dyes are also an important element of this business, so it is a supplier to other companies.
4. Mechanical engineering

What do capital goods jobs pay in Mechanical engineering industry
Mechanical engineering produces construction equipment and other necessary equipment used in the production of products. Manufacturing equipment produced in most countries is supplied to foreign companies for use in the manufacture of their specialised products.
5. Steel industry
The steel industry is primarily concerned with the production and reuse of steel waste.
6. Automotive industry

What do capital goods jobs pay in Automotive industry
In the automotive industry you can get parts for everything from bicycles to pick-up trucks and cars sold to companies that use these materials to build motorbikes and cars.
Understanding capital goods
Capital goods are called tangible assets because they are physical in nature. Capital goods are assets that companies use to produce products that other businesses can use to create finished goods. Manufacturers of cars, aircraft and equipment belong to the capital goods sector because their products are subsequently used by companies engaged in production, delivery and other services. In other words, capital goods do not create satisfaction (called utility in economics ) for the purchaser per se, but instead are used to produce a final product that does produce satisfaction.
Depreciation
Capital goods that a business does not consume in one year of production cannot be fully deducted as a business expense in the year of purchase. Instead, they must be depreciated over their useful lives, with the company receiving partial tax deductions allocated to the years in which the capital goods are used. This is done through accounting methods such as depreciation .
Depreciation accounts for the annual loss in value of a tangible asset over its useful life . Depreciation helps a company generate income from an asset by only writing off a portion of it each year. Depreciation of an asset means that the annual cost reduces income or net profit, creating lower taxable income and tax savings for the company.
Depletion
If a company extracts natural resources such as timber, depletion is the accounting method used to allocate the value of these natural resources as they are depleted or used in the business. Depletion can be calculated using cost depletion or percentage depletion.
For example, when deducting the value of standing timber, taxpayers should use the depletion method based on the total number of units recoverable and the number of units sold during the tax year. The depletion percentage estimates the value of the materials as a percentage of the company's gross income during a given year.
Types of capital goods
Capital goods are not necessarily fixed assets such as machinery and production equipment. Industrial electronics produce a wide range of devices which are capital goods. They can range from small assemblies of wiring harnesses to respirators for air purification and high-resolution digital imaging systems. Capital goods are also produced for the service industry. Hair clippers used by hairdressers, paints used by painters, and musical instruments played by musicians are among the many types of capital goods purchased by service suppliers.
Capital goods are a class of capital goods that does not include aircraft and goods produced for the Ministry of Defence, such as automatic rifles and military uniforms. The Census Bureau's monthly Preliminary Report on Durable Goods Orders includes data on purchases of capital goods, also known as capital goods, for capital expenditure. This information is closely watched as a forward-looking indicator of the extent to which companies plan to expand. Durable goods are goods with an expected useful life of at least three years.
Capital goods versus consumer goods
Consumer goods are finished products that consumers buy as a result of the production process. Although consumer goods have different classifications, examples of consumer goods include milk, household appliances and clothing.
Capital goods versus consumer goods
Conversely, capital goods are usually not sold to consumers, but instead are used to produce other goods that may be sold to consumers. However, there are capital goods that may also be consumer goods, such as aeroplanes, which are used by airlines but also by consumers.
Examples of capital goods
Below are some examples of capital goods that are used in different industries, as well as examples of goods that can be both capital goods and consumer goods.
Capital goods
- Plants or conveyor equipment used to produce cars and trucks
- Machinery and technology
- Infrastructure types such as trains and cable or broadband lines
- Coffee machines used in coffee shops
Capital and consumer goods
- Cars used by a transport company would be capital goods, but to a family they would be consumer goods.
- Ovens used in a restaurant would be a valuable commodity, but they could also be a consumer good.
- Computers could be used by companies, but they could also be a consumer product.
- Landscaping equipment could be used by landscape companies and consumers.
Conclusion
The capital goods industry is a great option for those who want to become part of the international supply chain while earning a lot of money.
There are many great careers to pursue in capital goods as they make up a large part of every economy. Of course, just because you know about these jobs doesn't mean you'll get the job easily. Companies don't stand in line to hire new graduates. That is why education is important. You should always try to keep learning. There's a lot of valuable information out there, and if you can combine that with good work experience, you'll be set for success.
The essentials you needed to know before starting a career in the capital goods industry have been outlined in this article. Solutions for all your questions and concerns should have been provided to you, and you should feel more confident than ever.