In Software Development
DLT is the technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but it has many other applications beyond that. In this post, we'll explore some examples of DLT, applications of DLT, and courses that can help you learn more about this exciting technology.

Editor
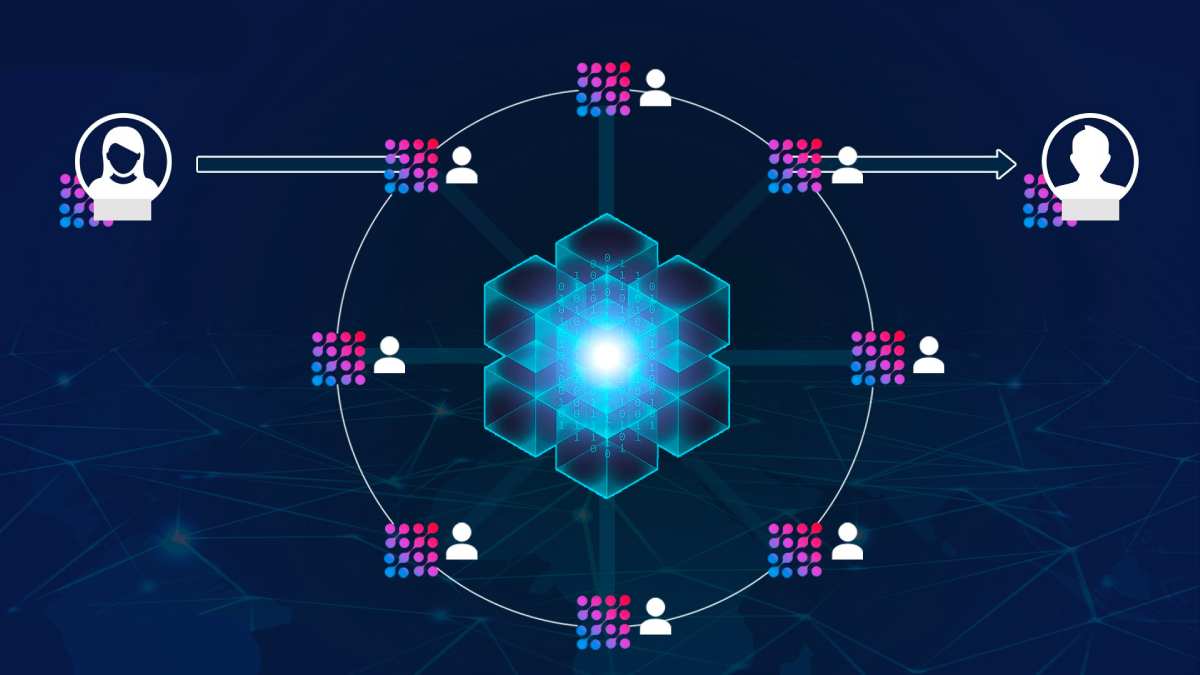
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a type of database that is spread across multiple nodes in a network. Each node has a copy of the database, and the database is updated simultaneously across all nodes.
What is Distributed Ledger Technology?
DLT is a type of database that is distributed across multiple nodes in a network. Each node has a copy of the database, and the database is updated simultaneously across all nodes. This means that there is no central authority controlling the database, and every participant in the network has a copy of the same information.
DLT is different from traditional databases in several ways. First, it is decentralized, which means that there is no central authority controlling the database. Second, it is immutable, which means that once data is added to the database, it cannot be deleted or changed. Third, it is transparent, which means that every participant in the network can see the same information. Finally, it is secure, which means that it is difficult for hackers to tamper with the data.
DLT vs traditional databases
| Feature | Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) | Traditional Databases |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Data is distributed and stored across multiple nodes in the network | Data is stored in a centralized server |
| Data Sharing | All parties on the network can access and share data as long as they have permission | Access to data is restricted to those with permission |
| Security | DLT uses cryptography and consensus algorithms to secure the network | Traditional databases rely on firewalls and access control lists to secure data |
| Transparency | All transactions on the network are visible to all parties | Transactions are only visible to those with access to the database |
| Immutability | Once data is recorded on the network, it cannot be altered or deleted | Data can be altered or deleted by those with appropriate permissions |
| Scalability | DLT can scale to accommodate a large number of nodes in the network | Traditional databases may struggle with scalability as the number of users and data grows |
| Speed | DLT can process transactions faster than traditional databases in some cases, especially when there are multiple parties involved | Traditional databases may be faster when only one user is accessing the data |
Distributed Ledger Technologies: Examples
There are several examples of DLT, each with its own unique characteristics and use cases. Some of the most well-known examples include:
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is the first and most well-known example of a cryptocurrency that uses DLT. Bitcoin is based on the blockchain, which is a type of DLT that is designed to be immutable, transparent, and secure.
Ethereum
Ethereum is a blockchain platform that allows developers to build decentralized applications (dApps) on top of it. It uses a different type of DLT called the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
Hyperledger Fabric
Hyperledger Fabric is a DLT that is designed for use in enterprise settings. It is a permissioned blockchain, which means that only authorized participants can access the network.
Other examples
| Project Name | Industry | Technology Used | Launch Year | Funding Raised (USD) | Number of Employees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chain | Finance | Bitcoin, Ethereum | 2014 | $43.7 million | 51-200 |
| Hyperledger Fabric | Business | Ethereum, IBM Blockchain | 2015 | N/A | 501-1000 |
| IOTA | IoT | Tangle | 2015 | $520 million | 51-200 |
| Ripple | Finance | XRP Ledger | 2012 | $93.6 million | 501-1000 |
| VeChain | Supply Chain | VeChainThor | 2015 | $62 million | 201-500 |
| BigchainDB | Business | MongoDB, IPDB | 2013 | $3.7 million | 11-50 |
| Hedera Hashgraph | Business | Hashgraph | 2017 | $124 million | 11-50 |
| NEM | Finance | NEM | 2015 | N/A | 11-50 |
| EOSIO | Business | EOSIO | 2017 | $4.2 billion | 51-200 |
| Corda | Finance | Corda | 2016 | $20 million | 51-200 |
Distributed Ledger Technologies: Applications
DLT has many applications beyond cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Some of the most promising applications include:
-
Supply Chain Management: DLT can be used to track products as they move through the supply chain. This can help reduce fraud, increase transparency, and improve efficiency.
-
Healthcare: DLT can be used to securely store and share medical records. This can help reduce errors, increase efficiency, and improve patient outcomes.
-
Voting: DLT can be used to create a transparent and secure voting system. This can help reduce fraud and increase trust in the electoral process.
Distributed Ledger Technologies: Courses
If you're interested in learning more about DLT, there are several online courses that can help you get started. Some of the most popular courses include:
-
Blockchain Basics: This course, offered by edX, provides an introduction to blockchain and DLT. It covers the basics of how blockchain works, as well as some of the most common use cases.
-
IBM Blockchain Foundation for Developers: This course, offered by IBM, provides a more in-depth look at DLT. It covers topics like smart contracts, Hyperledger Fabric, and blockchain security.
-
Distributed Ledger Technology: This course, offered by Coursera, provides an overview of DLT and its applications. It covers topics like blockchain consensus algorithms, privacy, and scalability.
Wrap-Up
Distributed ledger technologies are changing the way we do business and manage transactions. From banking and finance to supply chain management and healthcare, the potential applications of DLTs are vast and varied. As more companies and organizations explore the benefits of this technology, it is likely that we will see even more innovative uses for distributed ledgers in the future.
Whether you are looking to learn more about DLTs for personal or professional reasons, there are many resources available. From online courses to industry events and conferences, there are numerous opportunities to gain knowledge and network with others in the field. By staying up-to-date on the latest developments in distributed ledger technology, you can position yourself for success in a rapidly changing digital landscape.